Huawei H12-323_V2.0-ENU Übungsprüfungen
Zuletzt aktualisiert am 08.03.2026- Prüfungscode: H12-323_V2.0-ENU
- Prüfungsname: HCIP-WLAN V2.0
- Zertifizierungsanbieter: Huawei
- Zuletzt aktualisiert am: 08.03.2026
In NaviAC networking, LocalAC and NaviAC cannot establish a CAPWAP tunnel. What are the possible causes of this failure? (Multiple choice)
- A . The CAPWAP source addresses of the Local AC and Navi AC are unreachable on the network.
- B . The CAPWAP source address is not specified in the Local AC
- C . CAPWAP source address is not specified in Navi AC
- D . The Navi AC has not applied for an AP license
In the LeaderAP networking mode, FITAP is managed by LeaderAP, and service data traffic needs to be forwarded uniformly through LeaderAP
- A . True
- B . False
In the stadium hall scene, the floor heights mainly include ordinary areas (3 meters) and high-ceiling areas (greater than 6 meters).
Which of the following descriptions of the network planning solutions for these two areas is wrong?
- A . Both areas can be covered by omnidirectional APs
- B . When deploying APs in both areas, they should be as far away from the stadium seating area as possible.
- C . If the floor height is between 3 and 6 meters, it is recommended to place APs on the ceiling at a spacing of 18 to 25 meters.
- D . For areas with a floor height of more than 6 meters, it is recommended that APs be wall-mounted, deployed at intervals of 18 to 25 meters, and at least 3 meters away from load-bearing columns.
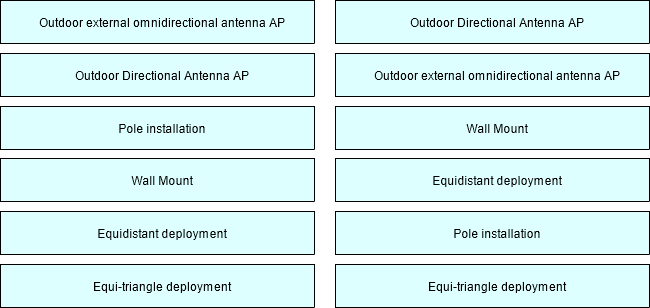
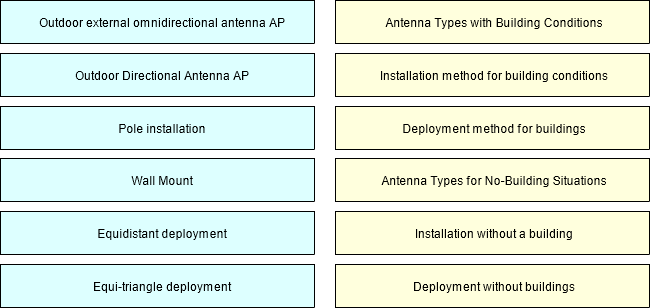
When designing the network plan for an outdoor parking lot, there may be two situations as shown in the following figure (with buildings and without buildings). Please match the antenna type, installation method and AP deployment method recommended by the following network plan with the two situations. 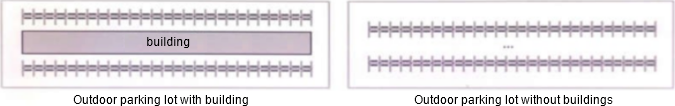
In existing network applications, there is a type of terminal that has poor roaming initiative, which is mainly manifested in that it always "sticks" to the AP it initially associated with. Even if the terminal moves far away from the currently associated AP, the signal is weak, and the rate is low, this type of terminal still cannot roam to other neighboring APs with better signals.
This type of terminal is called a sticky terminal. Which of the following is a roaming optimization solution for sticky users?
- A . 802.11r fast roaming
- B . Layer 3 roaming
- C . PMK Fast Roaming
- D . Smart Roaming
In a certain enterprise office WLAN network, network engineers found that many APs were offline for a long time after being disconnected, or were offline again after being online.
Which of the following could be the cause of this failure?
- A . The AP’s peer device has SIP enabled, but the AP has not.
- B . The AP is not assigned an IP address
- C . Insufficient license resources
- D . WAC does not support this AP type
Which of the following scenarios is suitable for using the ACU2 board as a wireless controller? (Multiple choice)
- A . The network is large and there is a need for further expansion in the future
- B . Small and medium-sized, integrated networking scenarios
- C . Scenarios with limited rack slot resources
- D . Scenario with abundant rack slot resources
WLAN networks transmit data through wireless signals. As the transmission distance increases, the wireless signal strength will become weaker and weaker, and there will be overlapping interference between adjacent wireless channels. These will reduce the quality of wireless network signals and even make the wireless network unusable.
- A . True
- B . False
A large enterprise deployed a WLAN network based on the cloud campus network solution, and centrally managed and maintained cloud APs through iMaster NCE-Campus, reducing network deployment and operation costs.
After the AP is deployed, engineers need to switch its working mode. Which of the following methods can be used to achieve this? (Multiple choice)
- A . Switch via the CloudCampus app
- B . Switch via command line
- C . Switching through PHCP configuration Option 43
- D . Switch via the registration center
In WLAN networks, the 24 GHz frequency band is divided into 14 overlapping channels with a frequency width of 20 MHz (except 802.11b). Which of the following channels is a commonly used non-overlapping channel in existing networks?
- A . 1, 4, 7 and 13
- B . 1, 7, 9 and 13
- C . 1, 5, 9 and 13
- D . 1, 3, 5 and 9