PECB ISO-9001 Lead Auditor Übungsprüfungen
Zuletzt aktualisiert am 08.03.2026- Prüfungscode: ISO-9001 Lead Auditor
- Prüfungsname: QMS ISO 9001:2015 Lead Auditor
- Zertifizierungsanbieter: PECB
- Zuletzt aktualisiert am: 08.03.2026
An audit team leader arrives at a printing organisation to carry out a Stage 2 audit for a certification body. At a meeting with the Quality Manager, she is told that they have won their biggest contract from a computer manufacturer to print and compile computer documentation packages. They have leased the unit next door for space reasons but have never worked in this sector before. The Quality Manager wants the ISO 9001 certificate to cover the new contract.
Which one of the options is the correct response by the auditor?
- A . Do you realise that this involves an extension to the scope of the audit and will require an application process?
- B . How can we audit this area when we do not have an IT specialist in the team?
- C . Would you like a separate certificate for the IT packages to show your new client?
- D . Would you mind writing to my programme manager with this request?
You are conducting a third-party audit to ISO 9001 and interviewing the Training Manager. She explains that training is more important than ever because the organisation has had to reduce the number of staff employed. Many of the remaining staff are now required to be ‚multi-skilled‘. You ask to see plans for the multi-skilling training and are shown plans that look comprehensive, and include both ‚on the job" training and internal and external training courses.
The records indicate that several staff required parts of their training to be repeated one month after the first training was provided. You ask why this was needed and are told that an investigation of customer complaints identified that several staff members did not complete certain tasks in the correct manner. The extra training was therefore recommended as a corrective action.
Based on this interview, which two of the following audit trails would be the most appropriate to follow?
Select the two most appropriate audit trails from the following.
- A . Ask if customer complaints had ceased since the multi-skilled training finished.
- B . Ask the members of staff whether they found the training received useful.
- C . Assess whether Quality objectives are being met.
- D . Determine whether customers were consulted about the risks associated with the multi-skilling training.
- E . Determine whether management has assessed the impact of staff reduction on the organisation’s ability to meet its objectives.
- F . Review records to assess if all planned training has been completed.
A Health Trust has contracted with Servitup, a catering services organisation that has been certified to ISO 9001 for one year. It provides services to 10 small rural hospitals in remote locations involving the purchase and storage of dry goods and fresh produce, preparing meals, and loading heated trolleys for Ward Service by hospital staff. You, as auditor, are conducting the first surveillance audit at one site with the Deputy Catering Manager (DCM).
DCM: "IO 9001 for one year. It provides service apologise for the absence of the Catering Manager. He has called in sick today and we are really short of staff."
You: "I see. It really shouldn’t affect the QMS so the audit can progress as normal."
DCM: "The Catering Manager set up the system. I’m afraid I’m not as familiar with it as he is."
You: "OK, let’s start with the Quality Policy.
What are the main issues for the QMS here?"
DCM: "Give me a minute. I need to look at the Quality Policy on the noticeboard in his office."
As the audit progresses, it is clear that the DCM has a very low knowledge of the QMS. He continually has to look up the answers to your questions
or ask staff members about their processes. You decide to raise a nonconformity.
Select one of the following options that best describes the nonconformity.
- A . As a member of the management team, the Deputy Catering Manager is not sufficiently aware of the QMS.
- B . The Deputy Catering Manager is not competent to manage the QMS.
- C . The effectiveness of the QMS depends on the Catering Manager being present on site.
- D . The Quality Policy only exists as a document in the Catering Manager’s office.
You have been nominated audit team leader of a third-party audit.
Which of the following could be the two most relevant objectives of this audit?
- A . Evaluate the satisfaction interested parties
- B . Evaluate the effectiveness of the management system
- C . Identify the need of resources
- D . Evaluate the capability of the management system to establish and achieve objectives
- E . Identify opportunities for improvement
- F . Evaluate the benefits obtained since the implementation of the management system
During a third-party audit of a pharmaceutical organisation (CD9000) site of seven COVID-19 testing laboratories in various terminals at a major international airport, you interview the CD 9000’s General Manager (GM), who was accompanied by Jack, the legal compliance expert. Jack is acting as the guide in the absence of the Technical Manager due to him contracting COVID-19.
You: "What external and internal issues have been identified that could affect CD9000 and its quality management system?"
GM: "Jack guided us on this. We identified issues like probable competition of another laboratory organisation in the airport, legal requirements on COVID-19 continuously changing, the shortage of competent laboratory analysists, the epidemic declining soon, shortage of chemicals for the analysis. It was quite a good experience."
You: "Did you document these issues?"
GM: "No. Jack said that ISO 9001 does not require us to document these issues."
You: "How did you determine the risks associated with the issues and did you plan actions to address them?"
GM: "I am not sure. The Technical Manager is responsible for this process. Jack may be able to answer this question in his absence."
Select two options for how you would respond to the General Manager’s suggestion:
- A . I would ask to audit the Technical Manager by phone.
- B . I would ask for a different guide instead of the legal compliance expert.
- C . I would look for evidence that the actions resulting from the risk assessment had been taken.
- D . I would ask the consultant to leave the meeting since he is not an employee of the organisation.
- E . I would delay the audit until the return of the technical manager
- F . I would not accept the legal compliance expert answering the question.
DRAG DROP
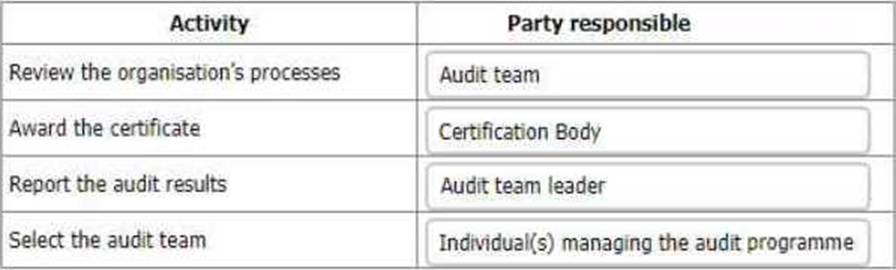
In the context of a third-party audit, match the activity with the party responsible in relation to the audit process.

To complete the table, click on the blank section you want to compete so that it is highlighted in red, and then did on the applicable text from the options below. Alternatively, drag and drop each option to the appropriate blank section.
Which two of the following auditors would not participate in a first-party audit?
- A . An auditor employed by an external consultancy organisation
- B . An auditor from an interested party
- C . An auditor trained in-house
- D . An auditor trained in the IRCA scheme
- E . An auditor certified by IRCA
- F . An auditor from a customer
DRAG DROP
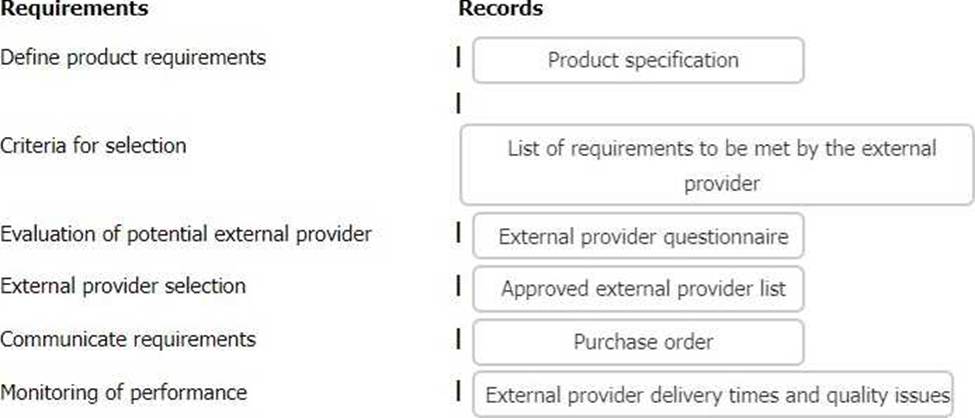
The following list gives examples of records that may be evidence of how an organisation has fulfilled the requirements of clause 8.4 of ISO 9001. Match the records to the appropriate requirement of clause 8.4.
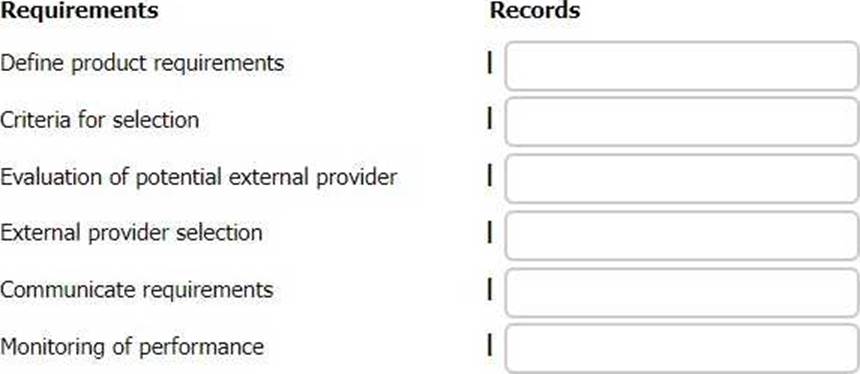
To complete the table click on the blank section you want to complete so it is highlighted in red and then click on the appropriate record from the option listed. Alternatively, drag and drop the appropriate record to the requirement of clause 8.4 that applies.

A Health Trust has contracted with Servitup, a catering services organisation which has been certified to ISO 9001 for 1 year. It provides services to ten, small rural hospitals in remote locations involving purchase and storage of dry goods and fresh produce, preparing meals and loading heated trolleys for ward service by hospital staff. An auditor is conducting the first sole surveillance audit at one site with the Deputy Catering Manager (DCM).
At the closing meeting attended solely by the DCM, the auditor informs him that he has found numerous gaps in the QMS processes which lead him to consider recommending suspension of the organisation’s certification. He is particularly concerned with the evidence that patient health is being adversely affected by produce stored beyond its safe consumption date, poor kitchen hygiene and undercooked meals. The DCM says that he cannot make any decisions about these issues in the absence of the Catering Manager due to illness but will write everything down and report to the Catering Manager.
Which two actions should you take in the context of the audit?
- A . Close the meeting immediately after the DCM’s response and advise that the issues will be addressed at the next surveillance visit.
- B . Call the individual(s) managing the audit programme to explain the situation and recommend immediate suspension of certification to protect the integrity of the Certification Body.
- C . Continue with the meeting, present the audit conclusions and inform the DCM that the organisation will receive the audit report in due course.
- D . Conclude the meeting early and advise that it will be rescheduled once the Catering Manager has returned to work.
- E . Recommend that all personnel should be given urgent in-depth training in the QMS.
- F . Thank the DCM for his time and express an expectation that improvements will be made in the QMS.
A small deaning services organisation is about to start work on a hospital dleaning contract for the local Health Trust. You, as auditor, are conducting a Stage 2 audit to ISO 9001 and review the contract with the Service Manager. The contract requires that a cleaning plan is produced. You: "How was the cleaning plan for the contract developed?" Service Manager: "We have a basic template that covers the materials, labour requirements and cleaning methods to be employed. Some of that is specified by the customer." You: "How does the plan deal with locations like the intensive care wards and the operating theatres, which are included in the contract?" Service Manager: "The basic plan covers general wards, but we will do more frequent cleaning in those areas if the hospital requests it." You: "Are you aware of the regulatory requirements for cleaning standards in hospitals?" Service Manager: "No. We depend on the hospital to look after that side of things in the contract." You decide to raise a non-conformity against section 8.2.2.a.1 of ISO 9001. You decide to raise another non-conformity against section 8.2.4 of ISO 9001 when finding that the cleaning plan was amended without the agreement of the Health Trust. A different cleaning chemical was substituted to that specified in the contract. At the follow- up audit, the corrective action proposed was to "obtain a concession from the Health Trust for use of the new chemical."
Which one of the following options is the reason why you did not accept this action taken?
- A . The substitute chemical has not been used before in the Health Trust.
- B . The action assumes that the Health Trust will agree to the change.
- C . Staff have not been trained in the use of the new chemical.
- D . The process for making changes to the contract has not been addressed.
- E . The substitute chemical may not be as effective as the original.