PECB ISO-9001 Lead Auditor Übungsprüfungen
Zuletzt aktualisiert am 08.03.2026- Prüfungscode: ISO-9001 Lead Auditor
- Prüfungsname: QMS ISO 9001:2015 Lead Auditor
- Zertifizierungsanbieter: PECB
- Zuletzt aktualisiert am: 08.03.2026
Select six of the activities that are specifically required by ISO 17021-1 as part third-party (Certification Body) surveillance audit processes.
- A . Audit use of certification marks on marketing materials.
- B . Review changes to the QMS since last visit.
- C . Confirm effectiveness of internal audit and management review.
- D . Complete a full document review of the quality management system.
- E . Failing to meet financial responsibilities.
- F . Review the status of previously raised findings and audit effectiveness of any outstanding findings.
- G . Review the calibration status of the instrumentation.
- H . Verify legal compliance.
- I . Handling of customer complaints since last visit.
- J . Conduct a minimum number of annual surveillance audits during the certification period.
DRAG DROP
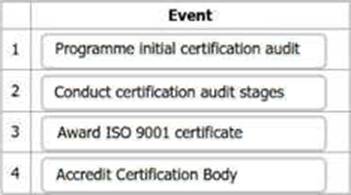
State the correct sequence of events in the certification process for an organisation to obtain third-party accredited certification to ISO 9001.
To complete the sentences click an the blank section you want to compete so itis highlighted in red and then click on the applicable text from the options below. Alliteratively, drag and drop the options to the appropriate blank section.

An audit team leader arrives at a printing company to carry out a Stage 2 audit for a certification body. At a meeting with the Quality Manager, she is told that they have won their biggest contract from a computer manufacturer to print and compile computer documentation packages. The Quality Manager wants the ISO 9001 certificate to cover the new contract.
During the audit, a team member found that some print jobs had been rejected by several clients over some months due to spelling errors in the print run. The Print Manager blames the new employees they had to take on because of a big contract.
The auditor finds that the responsibility for checking spelling errors is placed on the printer that sets up the print run.
In line with the policy of the certification body, the audit team raise improvement opportunities in the audit report.
Which three of the following options would represent acceptable opportunities for improvement in the report?
- A . Operational planning activities may benefit from a clearer risk-based approach.
- B . The organisation needs to delay its certification to gain more experience of the QMS.
- C . The responsibility for checking printing needs to be independent of the operators.
- D . A business consultant can be recommended for advice on improving operations.
- E . A plan to determine why the errors occur and to prevent them.
- F . An intensive training plan that involves all production personnel.
- G . The recruitment process to include spelling tests to filter out unsuitable candidates.
- H . More process time needs to be allocated to the new employees.
Noitol is an organisation specialising in the design and production of e-learning training materials for the insurance market. During an ISO 9001 audit of the development department, the auditor asks the Head of Development about the process used for validation of the final course design. She states that they usually ask customers to validate the product with volunteers. She says that the feedback received often leads to key improvements.
The auditor samples the design records for a recently completed course for the 247 Insurance organisation. Design verification was carried out but there was no validation report. The Head of Development advises that this customer required the product on an urgent basis, so the validation stage was omitted. When asked, the Head estimates that this occurs about 50% of the time. She confirms that they always ask for feedback and often make changes. There is no record of feedback in the design file for the course.
The auditor raises a nonconformity against ISO 9001.
Which one of the following options is the basis for the nonconformity?
- A . 8.3.5 – The improvements made to course designs are not documented. Feedback from customers is not always actioned.
- B . 8.3.2.c – Design planning does not include design validation. Design verification is part of the planning process.
- C . 8.3.4.d – Design validation is not always conducted. It is omitted about half of the time.
- D . 8.6 – Course materials are released without proper approval. A course for 247 Insurance was released on an urgent basis.
DRAG DROP
You are carrying out an audit at a single-site organisation seeking certification to ISO 9001 for the first time. The organization manufactures cosmetics for major retailers and the name of the retailer supplied appears on the product packaging. Sales turnover has increased significantly over the past five years.
You are interviewing the new Product Development Manager. You note that a software application called SWIFT is used to help control the product development process.
You have gathered audit evidence as outlined in the table. Match the ISO 9001 clause 8.3 extracts to the audit evidence.

To complete the table click on the blank section you want to complete so it is highlighted in red and then click on the Iso 9001 cause 8.3 extracts listed below. Alternatively, drag and drop each clause to the audit evidence that applies.

XYZ Corporation is an organisation that employs 100 people. As audit team leader, you are conducting a certification audit at Stage 1. When reviewing the quality management system (QMS) documentation, you find that quality objectives have been set for every employee in the organisation except top management.
The Quality Manager complains that this has created a lot of resistance to the QMS, and the Chief Executive is asking questions about how much it will cost. He asks for your opinion on whether this is the correct method of setting objectives.
Three months after Stage 1, you return to XYZ Corporation to conduct a Stage 2 certification audit as Audit Team Leader with one other auditor. You find that the Quality Manager has cancelled the previous quality objectives for all employees and replaced them with a single objective for himself. This states that "The Quality Manager will drive multiple improvements in the QMS in the next year". The Quality Manager indicates that this gives him the authority to issue instructions to department managers when quality improvement is needed. He says that this approach has the full backing of senior management.
He shows you the latest Quality Improvement Request that was included in the last management review.
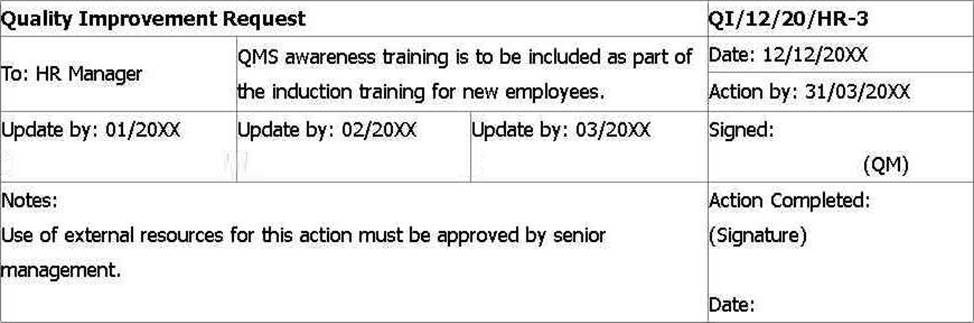
After further auditing, the issues below were found. Select three statements that apply to the term ‚audit trail‘
- A . Decisions on improvement action timescales not involving departmental managers.
- B . Evaluation of the results of the improvement action not always documented by the Quality Manager.
- C . Limited knowledge of the content of Quality Improvement Requests by departmental staff.
- D . Quality improvements not aligning with the quality policy.
- E . The single quality objective set for the organisation by the Quality Manager.
- F . Top management claim not to be aware of the improvement request (QI/12/20/HR-3) initiated by the Quality Manager.
DRAG DROP
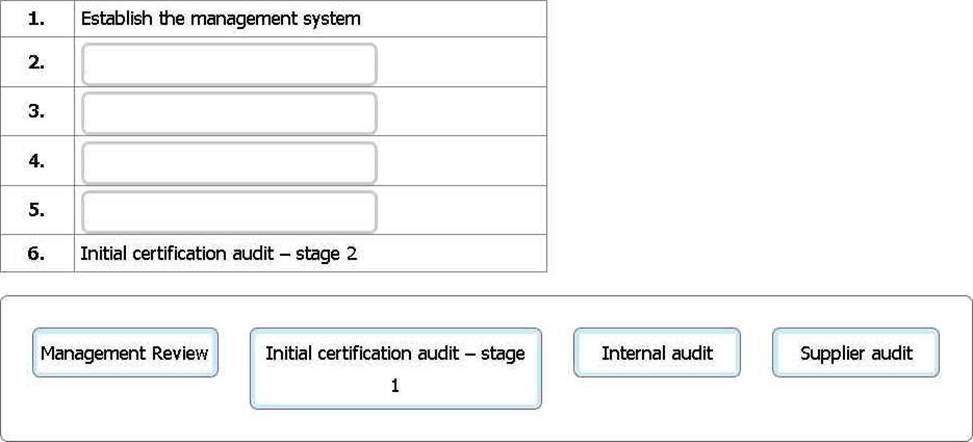
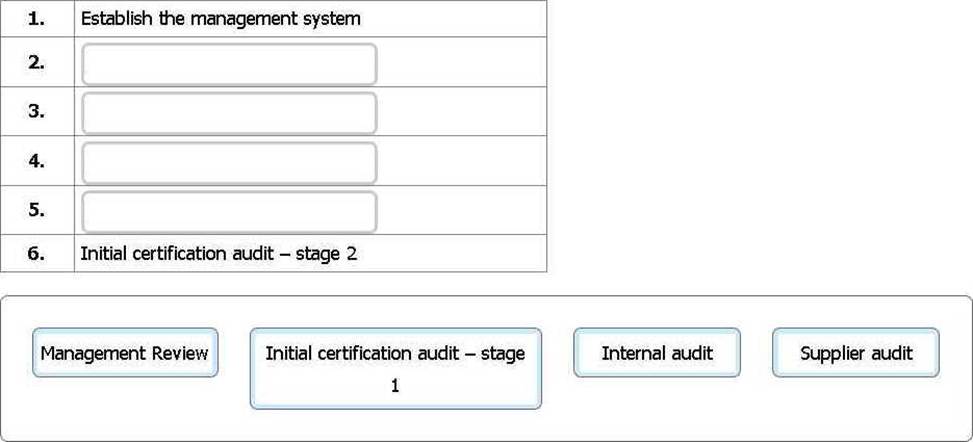
An organisation wants to certify their ISO 9001:2015-based QMS for the first time. Arrange the activities in the correct sequence from 2 to 5.
To complete the sequence, click on the blank section you want to complete so it is highlighted in red and then click on the applicable text from the options below. Alternatively, drag and drop the options to the appropriate blank section.
You are carrying out an annual audit at an organisation that has been certificated to ISO 9001 for two years. The organisation offers home security services. The scope of the quality management system covers alarm installation, alarm servicing, alarm monitoring and response. The business operates from a single office and employs subcontract installers and service technicians across the country.
You have just completed the opening meeting. You are interviewing the Managing Director (MD).
You: "I would like to gain an understanding of how the quality management system has been supporting your business and its strategic direction."
MD: "We are continuing to face difficult times. The market is extremely competitive, and customers typically look for the least expensive option when choosing home security services. We have not yet seen any business benefit from our quality management system."
You: "Tell me how you determine external and internal issues."
MD: "We use SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)."
You: "How have the outputs from your SWOT been used?"
Select two of the following audit trails would you take to explore the extent to which the SWOT analysis and the outputs from this have been used to enable the business to achieve the intended results(s) of its quality management system according to ISO 9001.
- A . Establish how many interested parties need to be consulted
- B . Establish how the organisation reviews information about external and internal issues
- C . Establish how the organisation shares information with external interested parties
- D . Establish what actions were taken to improve the QMS
- E . Establish whether the SWOT analysis has been reviewed by the procurement manager
- F . Establish whether the SWOT analysis is focussed solely on the QMS
Knowledge and skills are requirements of the auditor’s competence. Select two from the following topics of knowledge that apply to every member of an audit team auditing an ISO 9001 quality management system.
- A . Requirements of ISO 9001
- B . ISO 19011 Audit principles
- C . Organisation’s market sector
- D . Organisation’s invoicing and profits of the last 5 years
- E . Organisation’s processes
- F . Requirements of auditee’s interested parties other than customers
You, as auditor, are in dialogue with the quality lead and managing director of a small business that supplies specialist laboratory equipment and furniture.
You: "I’d like to look at how you manage change in the organisation.
What changes have you made as a business, say, over the last 12 months?"
Auditee: "We have made some strategic changes, the main one being that we no longer manufacture our own products in house."
You: "That sounds like quite a significant change.
What has been the impact of that?"
Auditee: "We now mainly sell other manufacturers‘ products, under their brand names, and have outsourced manufacture of our own brand products to one of our suppliers. Unfortunately, we had to make six members of our staff redundant. This represents about 20% of our workforce, so this has been quite a challenging time."
You: "I’m sure.
What were the reasons for making the change?"
Auditee: "Our manufacturing section was a small operation, and we struggled to cope with fluctuations in demand. During busy periods, we found it hard to meet lead times, and in quiet periods we had staff with little to do. This was having an impact on customer satisfaction and meant we had to charge premium prices that made our product uncompetitive."
You: "How did you go about the change?"
The auditor asks to speak to the purchasing manager about the selection of the subcontractor to manufacture the company’s own brand products.
You: "How did you choose a supplier to manufacture your products?"
Auditee: "We have had a long-term relationship with a supplier ABC Ltd – we gave them our design drawings, got them to complete a supplier questionnaire and run a couple of trial batches for us. We were happy with the result and we have used them ever since."
ISO 9001:2015, clause 8.4.1 outlines situations when controls need to be applied to externally provided processes, products and services.
Which one of the following situations is applicable to this scenario?
- A . Products and services for which the customer(s) supplies materials
- B . A process or part of a process is provided by an external provider as a result of a decision by the organisation.
- C . Products and services are provided directly to the customer(s) by external providers on behalf of the organisation.
- D . Raw materials from external providers are intended for incorporation into the organisation’s own products.